General Health
ProboMax
ProboMax
Couldn't load pickup availability
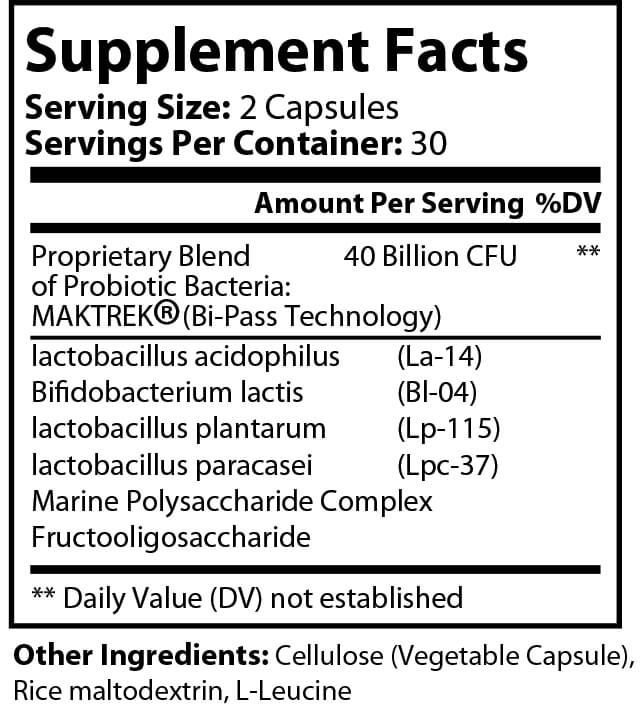
ProboMax is a blend of 4 strains (40 billion CFU/g) of Probiotic Bacteria. Our ProboMax supplement is designed to provide a high potency and balance of beneficial bacteria. By taking this product on a regular basis ProboMax can help assist in maintaining healthy intestinal flora. This supplement also contains FOS to help with acidophilus and bifidus.*
| Formula Purposes & Benefits |
|
ProboMax capsules are formulated to support athletic performance, enhanced gut micro biome, increased muscle mass, immune health, reduced cortisol levels, digestive health, cognitive function, and improved allergy symptoms. Our product is synthesized utilizing the latest scientific research and formulated with optimal ratios of collagen peptides to produce world class results. Our formula is third party independently tested for heavy metals, impurities, made in the USA, GMP certified, and produced in an FDA registered facility. 1% of the supplements on the market can match our world class standards. |
| Formula Ingredient Deck | Benefits Of Each Ingredient |
| Probiotic 40 Billion |
|
| Proper Use of This Supplement |
| Suggested Use: As a dietary supplement take two (2) capsules once a day. For best results, take 1 (one) capsule during the day and one (1) capsule in the evening. Repeat the process daily. Do not exceed two capsules per day. |
| Our Formula Vs Other Formulas on the Market. | |
| 1. Uses third party independently tested ingredients that are made in the USA, GMP certified, and made in an FDA registered facility. | 1. Source cheap ingredients from heavily polluted soils. Even “organic” supplements not third party tested have been removed by FDA due to high levels of heavy metals. |
| 2. High quality probiotic 40 billion strain in a purified and efficaciously dosed formula. | 2. Uses cheap sources of probiotic strains that are not alive at time of opening and contain high amounts of fillers and heavy metals. |
Sources:
- Park MS, Kwon B, Ku S, et al: The efficacy of bifidobacterium longum BORI and lactobacillus acidophilus AD031 probiotic treatment in infants with rotavirus infection. Nutrients 2017; 9:pii:E887.
- Hungin AP, Mulligan C, Pot B; European Society for Primary Care Gastroenterology, et al: Systematic review: probiotics in the management of lower gastrointestinal symptoms in clinical practice – an evidence-based international guide. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2013; 38: 864–886.
- Aragón F, Carino S, Perdigón G, et al: Inhibition of growth and metastasis of breast cancer in mice by milk fermented with lactobacillus casei CRL 431. J Immunother 2015; 38: 185–196.
- So SS, Wan ML, El-Nezami H: Probiotics-mediated suppression of cancer. Curr Opin Oncol 2017; 29: 62–72.
- Velez EM, Maldonado Galdeano C, Carmuega E, et al: Probiotic fermented milk consumption modulates the allergic process induced by ovoalbumin in mice. Br J Nutr 2015; 114: 566–576.
- Jäger, R., Mohr, A. E., Carpenter, K. C., Kerksick, C. M., Purpura, M., Moussa, A., Townsend, J. R., Lamprecht, M., West, N. P., Black, K., Gleeson, M., Pyne, D. B., Wells, S. D., Arent, S. M., Smith-Ryan, A. E., Kreider, R. B., Campbell, B. I., Bannock, L., Scheiman, J., Wissent, C. J., … Antonio, J. (2019). International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: Probiotics. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 16(1), 62. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-019-0329-0
- Hooper LV, Littman DR, Macpherson AJ: Interactions between the microbiota and the immune system. Science 2012; 336: 1268–1273.